https://www.itdev.co.uk/blog/pipelining-axi-buses-registered-ready-signals
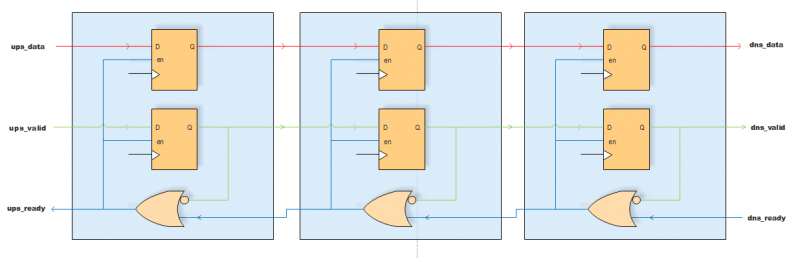
Above diagram shows the ready signal is not pipeline, which cause the timing closure issue when long dealy.
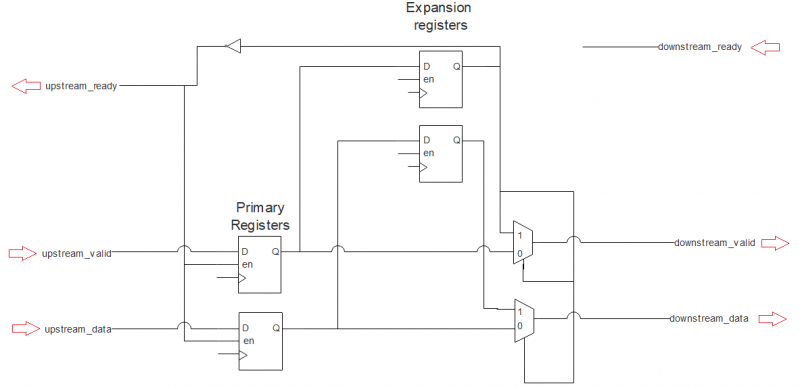
The next one shows the ready signal is pipeline. o_ready functional as current stoage has room to store the input data and when i_valid is active, data latched into r_data register. At this time, when i_ready is not active, the latched data shall go to skid register b_data.
1 //
2 // pipeline for the valid and ready data exchange with skid buffers
3 //
4 // Basically, the valid signal flags whether conresponding data are valid.
5 // i_valid flags i_data is valid.
6 // r_valid flags r_data is valid.
7 // b_valid flags b_data is valid.
8 // When b_valid is assert, put the b_data/b_valid as the priority output; otherwise, // put r_data/r_valid as output.
9 //
10
11 module axi_valid_ready_pipeline #(
12 parameter DATA_WIDTH = 8
13 ) (
14 input wire clk,
15 input wire rst_n,
16
17 input wire i_valid,
18 input [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] i_data,
19 output wire o_ready,
20
21 output wire o_valid,
22 output [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] o_data,
23 input wire i_ready
24 );
25
26 reg r_valid, b_valid;
27 reg [DATA_WIDTH-1:0] r_data, b_data;
28
29 always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
30 if (!rst_n) begin
31 r_valid <= 1'b1;
32 r_data <= 'b0;
33 b_valid <= 1'b1;
34 b_data <= 'b0;
35 end
36 else if (o_ready) begin // accept data if o_ready is high, mean either r or b register are ready to accept data
37 r_valid <= i_valid;
38 r_data <= i_data;
39 if (!i_ready) begin // when the next stage is not ready, store r registers data into b registers
40 b_valid <= r_valid;
41 b_data <= r_data;
42 end
43 end
44 else if (i_ready) begin // when next stage is ready, b valid shall be clean
45 b_valid <= 1'b0;
46 end
47
48
49 assign o_ready = ~b_valid; // when b_regiser is not taken, the o_ready set to 1.
50 assign o_valid = b_valid ? b_valid : r_valid;
51 assign o_data = b_valid ? b_data : r_data;
52
53
54 endmodule